Book — Non-fiction. By Clint Smith. 2021. 336 pages.
An examination of how monuments and landmarks represent — and misrepresent — the central role of slavery in U.S. history and its legacy today.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By Kate Masur. 2021.
The movement for equal rights in the decades before the Civil War.
Continue reading
The Union Army occupied the Sea Islands off the coast of South Carolina, freeing approximately 10,000 people who had been enslaved, starting what became known as the Port Royal Experiment.
Continue reading
Born on this day in Massachusetts, Charles Sumner was outspoken against slavery, for full recognition of Haiti, against the U.S.-Mexico War, for true reconstruction with land distribution, against school segregation, and much more.
Continue reading
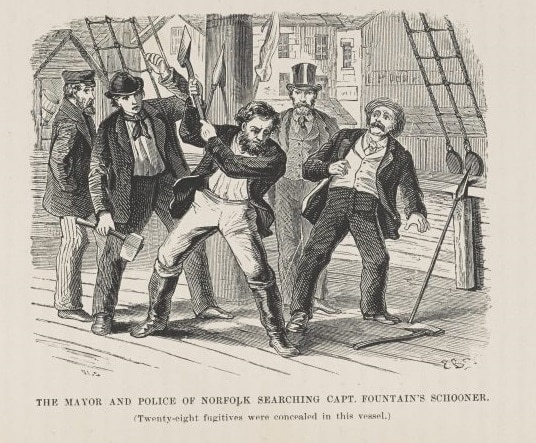
With escalating escapes of the formerly enslaved, the Virginia General Assembly responded to lobbying from slaveholders and human traffickers by making it harder for enslaved African Americans to escape on ships and by increasing penalties for anyone helping such freedom-seekers.
Continue reading
Freedom’s Journal was the first African American owned and operated newspaper in the United States.
Continue reading
Approximately ninety-six Africans held captive on the British slave ship Little George revolted against the ship’s captain and crew, eventually taking control of the entire ship.
Continue reading
Teaching Activity. By Ursula Wolfe-Rocca. 25 pages.
Students engage in an interactive activity with short excerpts from Martha Jones’ book to learn about the leading role of Black women in the fight for voting rights throughout U.S. history.
Continue reading
Digital collection. Records of the Bureau of Refugees, Freedman and Abandoned Lands, including new and unpublished records that document the formerly enslaved, freedpersons and their descendants.
Continue reading
Digital collection. Documents that help explain how Black people traversed the bloody ground from slavery to freedom between the beginning of the Civil War in 1861 and the beginning of Reconstruction in 1867.
Continue reading
Digital collection. Collections as data and machine learning project examining Jim Crow and racially-based legislation signed into law in North Carolina between Reconstruction and the Civil Rights Movement.
Continue reading
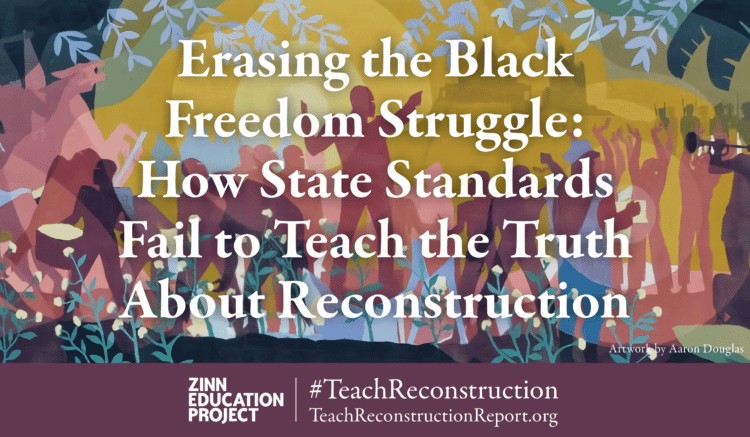
This month we released a printed edition of our national report, Erasing the Black Freedom Struggle: How State Standards Fail to Teach the Truth About Reconstruction. Thanks to the generous support of a donor, we can mail copies of the report to teacher educators, state and school district policymakers, and staff at historical societies.
Continue reading
Juneteenth — June 19th, also known as Emancipation Day — is one of the commemorations of people seizing their freedom from slavery in the United States. Yet, if the right wing has its way, it will be illegal to teach students about Juneteenth.
Continue reading
The Slave Revolt of 1842 — when dozens of enslaved Black people in Webbers Falls, Oklahoma fought back and briefly escaped from their Cherokee overseers — was the largest rebellion of enslaved people in Indian Territory history.
Continue reading
Teaching Activity. By Mimi Eisen and Ursula Wolfe-Rocca. 47 pages.
A follow-up lesson to “Reconstructing the South,” using primary source documents to reveal key outcomes of the Reconstruction era.
Continue reading
A community of armed Black men and women in Christiana, Pennsylvania successfully defended four Black people from capture, serving as a catalyst for further armed self-defense within the abolitionist movement.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By Gerald Horne. 2022. 632 pages.
A detailed history of counterrevolutionary forces in Texas state history.
Continue reading
On Saturday, March 25th, the Zinn Education Project offered a full-day workshop in Brattleboro on teaching Reconstruction.
Continue reading
Enslaved people on a Santo Domingo sugar plantation owned by the son of Christopher Columbus attempted to free themselves and take over the land in the earliest recorded slave uprising in the Americas.
Continue reading
In his 1860 speech commemorating radical abolitionist John Brown’s raid on Harper’s Ferry, Frederick Douglass argued that slavery would only end if the slave owner feared the violent retribution of the enslaved.
Continue reading
This was the largest uprising of the enslaved against their British overseers in Guyana. The uprising was ended after a few days, though it served as a catalyst for the abolition of slavery in British colonies soon thereafter.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By Olúfẹ́mi O. Táíwò. 2022. 280 pages.
Táíwò’s take on reparations and distributive justice has wide implications for views of justice, racism, the legacy of colonialism, and climate change policy.
Continue reading
Article. By Ana Rosado, Gideon Cohn-Postar, and Mimi Eisen. 2022. 44 pages.
The report includes assessments of education standards in all 50 states and the District of Columbia, along with findings and recommendations for how to improve instruction on Reconstruction.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By Howard Zinn, adapted by Rebecca Stefoff with additions by Ed Morales. Translated by Hugo García Manríquez. 2023. 608 pages.
A Spanish translation of the young adult version of the best-selling A People’s History of the United States.
Continue reading